Neuro Robotics is a powerful tool for testing brain theories and increasing our understanding of neuroscience. The robot controller is modelled after a specific aspect of the nervous system, and it includes all robots created to interact with or simulate human neurological systems.
The idaea of Neuro robotics for Rehabilitation dates back to the beginning of the previous century, and it is rapidly expanding. Rehabilitation hospitals have been incorporating robotics technologies into the daily treatment schedule of many patients. These interventions offer a more significant promise than just replicating traditional therapy, as they allow therapists to specify and monitor movement features such as speed, direction, amplitude, and joint coordination patterns and introduce controlled perturbations into therapy.
Neurological diseases causing motor/cognitive impairments are among the most common causes of adult-onset disability. More than one billion people are affected worldwide, and this number is expected to increase in upcoming years because of the ageing population.
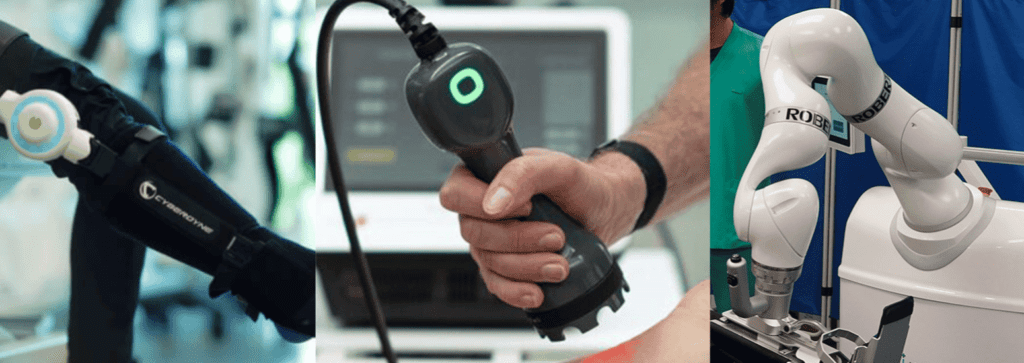
To fully realise the potential of robotic devices in Neurorehabilitation, it is necessary to understand better the specific aspects of movement that should be facilitated in rehabilitation. Robots for Neurorehabilitation are designed to support the administration of physical exercises to the upper or lower extremities to promote neuro-motor recovery.
The technological support of robotic-based therapy, non-invasive brain stimulation, and neural interfaces can aid rehabilitation therapy. Robotic Rehabilitation can reduce the burden of therapists by automating tedious and labour-intensive therapy and by adapting to the specific needs of the targeted individuals. Additionally, it can offer a multisensory rehabilitation experience when combined with other technologies, such as virtual and augmented reality. This way, it can provide additional sensory feedback to facilitate neuroplasticity and become more intuitive for individuals with cognitive deficiencies. Robotic technologies have demonstrated a clear potential for rehabilitation and daily use.
Robotic technology has gained significant traction in various industries, including physical therapy. By incorporating robotics into rehabilitation engineering, therapists can now provide targeted and personalised treatment plans, resulting in quicker recoveries and improved patient outcomes.
The advantages of robotic rehabilitation include targeted therapy, efficiency, improved safety, and detailed data. Robotic systems can perform repetitive tasks with consistent precision and minimal fatigue, allowing therapists to focus on analysing patient progress and adjusting treatment plans accordingly. Robotics technology captures detailed data during each session, providing therapists with objective measurements of a patient’s progress. This data-driven approach enables therapists to make informed decisions and tailor treatment plans to individual needs.
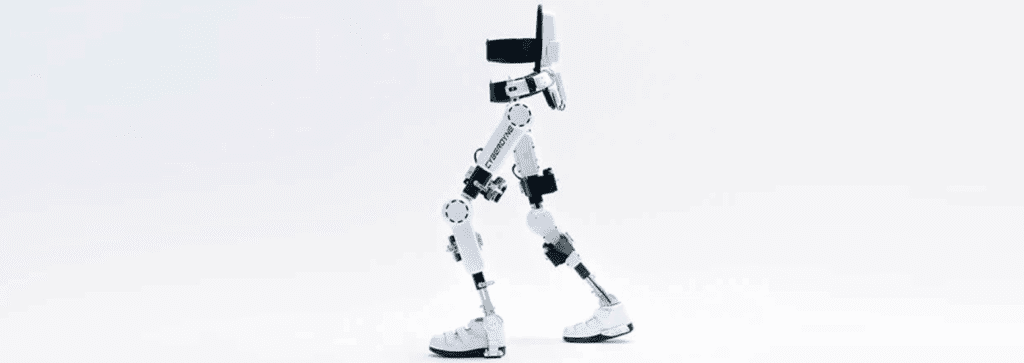
The versatility of robotics enables their application in several aspects of physical therapy, including robotic exoskeletons and robotic-assisted therapy. Exoskeletons are wearable robotic devices that aid individuals with impaired mobility to regain strength and independence, while robotic-assisted therapy involves the use of robotic devices to guide and support patients during therapeutic exercises. These devices can adjust resistance levels, track progress, and provide real-time feedback, making each session more engaging and productive.
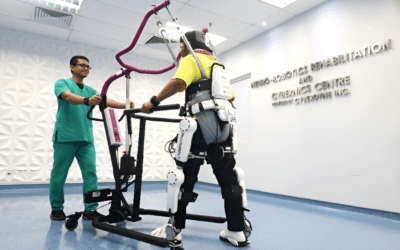
Integrating technology into rehabilitation programmes is essential, and during robotic gait training, patients are assisted with body-weight support and provided with a variety of sensory feedback options. This approach can promote early mobilisation by reducing the burden on therapists and allowing patients to engage in active movement sooner in their recovery journey.