Neurological Rehabilitation employs various strategies to enhance balance and coordination in patients with neurological conditions. Key methods include task-specific training, where patients practice real-life activities to refine movement patterns. Balance training exercises, such as standing on one leg, strengthen core and lower body muscles.
Cognitive-motor integration through dual-task training challenges the brain to manage multiple tasks, improving coordination. Virtual reality (VR) provides immersive environments for safe practice, increasing engagement. Robotic assistance offers guided movements and feedback, while functional electrical stimulation (FES) enhances muscle strength through electrical impulses.
Lastly, proprioceptive training improves body awareness by using uneven surfaces to stimulate balance responses. Together, these approaches significantly enhance the functional abilities of neurological patients.

Top 11 Neurorehabilitation Techniques to Improve Balance and Coordination
1. Task-Specific Training – Neurorehabilitation Balance Exercises
Targeted exercises that mimic daily activities help patients practice and refine their movement patterns, enhancing functional balance and coordination.
Neurorehabilitation balance exercises focus on improving stability and coordination through activities like weight shifting, single-leg standing, and guided movements on balance boards. These exercises help retrain the brain and body to improve postural control and reduce fall risk.
2. Balance Training – Balance Improvement
Structured balance exercises, such as standing on one leg or using balance boards, strengthen core and lower body muscles, improving stability and control.
3. Cognitive-Motor Integration
Activities that require simultaneous cognitive tasks, like dual-task training, enhance coordination by challenging the brain to manage multiple functions at once.

Immersive VR environments allow patients to practice balance and coordination in a safe, engaging context, which can improve motivation and retention of skills.
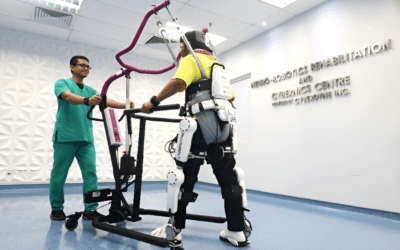
5. Robotic Assistance
Robotic devices can guide movements during rehabilitation exercises, providing feedback and support while encouraging the patient to actively engage their muscles.
6. Vestibular Therapy:
Head and eye movement exercises to aid spatial orientation and balance, especially for those with inner ear issues.
7. Strength and Flexibility Exercises:
Resistance bands, weightlifting, and stretching to build muscle support and flexibility.
8. Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
FES uses electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contractions, improving muscle strength and coordination, particularly in patients with limited voluntary movement.
9. Proprioceptive Training
Exercises that enhance body awareness and sensory feedback, such as standing on uneven surfaces, help improve balance by training the body to respond to different stimuli.
10. Gait Training:
Treadmill and overground walking with or without support to refine walking patterns and improve balance.
This involves exercises that retrain the brain and muscles to work together, improving movement accuracy and control. Techniques often include repetitive, targeted motions and fine motor tasks to enhance synchronization.
These approaches collectively foster improvements in balance and coordination, enhancing the overall functional abilities of neurological patients.
Conclusion
Exercises and therapies that target balance and coordination are crucial in Neurorehabilitation, as they help improve stability, mobility, and quality of life for patients with neurological conditions.
Through consistent practice and guidance from trained professionals, patients can regain functional independence, reduce the risk of falls, and enhance overall movement control.