Caregivers of individuals with neurodegenerative disorders, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, face a unique set of challenges. These struggles can impact their physical, emotional, and social well-being.

Here are some key issues caregivers often encounter:
1. Emotional and Mental Health Challenges
- Stress and Anxiety: The demands of caregiving can lead to significant stress and anxiety as caregivers manage the evolving needs of their loved ones.
- Depression: Many caregivers experience feelings of isolation, sadness, or hopelessness due to the emotional toll of their responsibilities.
2. Physical Strain
- Fatigue: Caregivers often face physical exhaustion from providing hands-on care, which may include lifting, transferring, and assisting with daily activities.
- Health Issues: Stress and physical demands can lead to health problems for caregivers, such as chronic pain, sleep disturbances, and cardiovascular issues.
3. Financial Burden
- Costs of Care: Managing a neurodegenerative disorder can be expensive, including medical bills, medications, and therapies, placing a financial strain on caregivers.
- Employment Challenges: Many caregivers may need to reduce work hours or leave their jobs entirely, impacting their income and job security.
4. Social Isolation
- Reduced Social Interaction: The time-consuming nature of caregiving often leads to decreased social activities, resulting in feelings of loneliness and isolation.
- Support System Strain: Caregivers may find that friends and family members don’t fully understand their situation, leading to a lack of emotional support.
5. Navigating Healthcare Systems
- Complex Care Coordination: Caregivers must often navigate complicated healthcare systems, coordinating appointments, treatments, and medications, which can be overwhelming.
- Communication Barriers: They may face challenges in communicating effectively with healthcare providers, especially if the patient has cognitive impairments.
6. Emotional Burden of Watching Decline
- Grief and Loss: Witnessing the decline of a loved one can lead to anticipatory grief, as caregivers cope with the emotional impact of losing the person they once knew.
- Guilt: Caregivers may experience guilt over feelings of frustration or resentment, questioning whether they are doing enough.
7. Uncertainty and Future Planning
- Unpredictable Progression: Neurodegenerative disorders often have unpredictable trajectories, making it difficult for caregivers to plan for the future.
- End-of-Life Issues: Caregivers may have to navigate complex decisions regarding end-of-life care, which can be emotionally taxing.
Caregivers of individuals with neurodegenerative disorders face multifaceted challenges that can significantly impact their lives. Recognizing these struggles is essential for providing appropriate support and resources, such as respite care, counseling, and support groups, to help caregivers manage their well-being while caring for their loved ones.
The best rehabilitation devices for effective and quicker recovery –
When it comes to rehabilitation, various devices can aid in effective and quicker recovery. Here are some of the best options

1. Therapeutic Ultrasound Machines
- Usage: Uses sound waves to promote tissue healing and reduce pain.
- Benefits: Increases blood flow and decreases inflammation.
2. Electrical Stimulation Units
- Types: TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation)
- Benefits: Reduces pain and improves muscle strength
3. Cold and Heat Therapy Devices
- Types: Ice packs, heating pads, and contrast therapy systems.
- Benefits: Cold reduces swelling; heat promotes blood flow and relaxation.
4. Compression Therapy Devices
- Types: Compression sleeves and pneumatic compression devices.
- Benefits: Reduces swelling and improves circulation.
5. Mobility Aids
- Types: Crutches, walkers, and canes.
- Benefits: Provides support and stability during recovery.
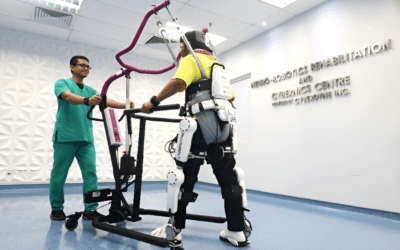
6. Rehabilitation Robots
- Usage: Assists with movement for stroke patients or those with mobility impairments.
- Benefits: Enhances recovery through guided movements.
7. Balance and Stability Trainers
- Types: Balance boards and stability balls.
- Benefits: Improves proprioception and core strength.
8. Resistance Training Equipment
- Types: Resistance bands and weight machines.
- Benefits: Builds strength and endurance gradually.
9. Virtual Reality Therapy
- Usage: Engages patients in simulated environments to improve movement and coordination.
- Benefits: Increases motivation and engagement in therapy.
10. Massage Tools
- Types: Foam rollers, massage guns, and handheld massagers.
- Benefits: Relieves muscle tension and enhances recovery.
Considerations
- Consultation: Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate devices based on specific needs and conditions.
- Personalization: Tailor the rehabilitation approach to individual recovery goals for the best outcomes.
Combining these devices with a structured rehabilitation program can significantly enhance recovery efficiency.
Neurodegenerative Disorders –
Neurodegenerative Disorders are a group of conditions characterized by the progressive degeneration of the structure and function of the nervous system.
Here’s an overview of some of the most common neurodegenerative disorders:
1. Alzheimer’s Disease
- Description: A progressive brain disorder that causes memory loss, cognitive decline, and changes in behavior.
- Symptoms: Memory loss, confusion, difficulty with language, and mood changes.
2. Parkinson’s Disease
- Description: A movement disorder caused by the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain.
- Symptoms: Tremors, stiffness, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability.
3. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Description: A severe disease that affects motor neurons, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy.
- Symptoms: Muscle cramps, weakness, difficulty speaking, swallowing, and eventually breathing.
4. Huntington’s Disease
- Description: An inherited condition characterized by the progressive breakdown of nerve cells in the brain.
- Symptoms: Movement disorders, cognitive decline, and psychiatric symptoms.
5. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Description: An autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, leading to communication issues between the brain and the rest of the body.
- Symptoms: Fatigue, difficulty walking, numbness, and coordination problems.
6. Frontotemporal Dementia
- Description: A group of disorders caused by progressive degeneration of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain.
- Symptoms: Changes in personality, behavior, and language skills.
7. Lewy Body Dementia
- Description: A type of progressive dementia characterized by the presence of Lewy bodies in the brain.
- Symptoms: Visual hallucinations, fluctuations in attention, and parkinsonism.
8. Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
- Description: A genetic disorder that leads to the degeneration of motor neurons, resulting in muscle weakness.
- Symptoms: Muscle wasting, difficulty in movement, and respiratory issues.
9. Prion Diseases
- Description: A group of rare, fatal brain disorders caused by misfolded proteins.
- Symptoms: Rapid cognitive decline, behavioral changes, and motor dysfunction.
Risk Factors
- Genetic: Family history can increase the likelihood of some disorders.
- Age: Many neurodegenerative diseases are more common in older adults.
- Environmental: Exposure to certain toxins may contribute to the risk.
Management and Treatment
- Medications: Some conditions have medications to manage symptoms (e.g., cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s).
- Therapies: Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help maintain function and improve quality of life.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and cognitive engagement may support brain health.
Research Directions
- Ongoing research is focused on understanding the underlying mechanisms, developing disease-modifying treatments, and exploring potential neuroprotective strategies.
Medical Treatment for Neurodegenerative Disorders –
Medical treatment for neurodegenerative disorders varies depending on the specific condition, its stage, and the individual patient’s needs. While many neurodegenerative diseases currently have no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and slowing disease progression.

Here’s an overview of treatment options for some common neurodegenerative disorders:
1. Alzheimer’s Disease
- Medications:
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors (e.g., Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine): Help increase levels of acetylcholine to improve memory and cognitive function.
- Memantine: Regulates glutamate levels to help with cognitive symptoms.
- Supportive Therapies: Cognitive stimulation, occupational therapy, and social engagement can improve quality of life.
2. Parkinson’s Disease
- Medications:
- Surgical Options: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) can be effective for some patients.
3. Supportive Care for ALS Patients with Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Medications:
- Riluzole: May slow the progression of the disease.
- Edaravone: An antioxidant that can help slow the decline in physical function.
- Supportive Care: Physical therapy, speech therapy, and nutritional support are crucial for managing symptoms.
4. Huntington’s Disease
- Medications:
- Tetrabenazine: Helps manage chorea (involuntary movements).
- Antidepressants and Antipsychotics: Can help manage mood and psychiatric symptoms.
- Supportive Care: Physical and occupational therapy can aid in maintaining function.
5. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs):
- Options include interferons (e.g., Avonex, Rebif), glatiramer acetate, and newer oral medications (e.g., Fingolimod, Dimethyl fumarate).
- Symptom Management: Medications for fatigue, muscle spasticity, pain, and bladder issues.
6. Frontotemporal Dementia
- Medications: No specific drugs, but antidepressants or antipsychotics may help manage behavioral symptoms.
- Supportive Care: Occupational and speech therapy can be beneficial.
7. Lewy Body Dementia
- Medications: Cholinesterase inhibitors can help with cognitive symptoms; care must be taken with antipsychotics due to sensitivity to these drugs.
- Supportive Therapies: Physical therapy and support groups can be beneficial.
8. Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
- Medications:
- Nusinersen: An antisense oligonucleotide that targets the SMN2 gene to increase SMN protein production.
- Onasemnogene abeparvovec: A gene therapy that provides a copy of the SMN1 gene.
- Supportive Care: Physical and occupational therapy, along with respiratory support as needed.
9. Prion Diseases (e.g., Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease)
- Medications: There are no effective treatments; care is generally supportive.
- Palliative Care: Focuses on comfort and quality of life.
General Supportive Measures
- Physical Therapy: Helps maintain mobility and strength.
- Occupational Therapy: Assists with daily living activities.
- Speech Therapy: Addresses communication and swallowing issues.
- Nutritional Support: Ensures adequate nutrition, especially for those with swallowing difficulties.
Research and Future Directions
- Ongoing research is focused on identifying disease-modifying treatments, investigating neuroprotective strategies, and exploring gene therapies. Participation in clinical trials may also be an option for some patients.
Conclusion
Effective management of neurodegenerative disorders requires a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach tailored to the individual’s needs. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers can help adapt treatment plans as conditions progress.
Rehabilitation Devices Perkeso –
PERKESO (the Social Security Organization of Malaysia) provides various rehabilitation services and devices to assist individuals recovering from injuries or disabilities.
Here are some rehabilitation devices that are commonly associated with rehabilitation programs under PERKESO:
1. Walking Aids
- Canes and Crutches: Assist individuals in maintaining balance and mobility.
- Walkers: Provide more stability for those who have difficulty walking.
2. Orthotic Devices
- Braces and Splints: Support weakened limbs or joints, improving function and stability.
- Ankle-Foot Orthoses (AFOs): Help with foot drop and improve walking ability.
3. Rehabilitation Robots
- Exoskeletons: Assist individuals with lower limb mobility, promoting independence in walking.
- Robotic arms: Aid in rehabilitation of upper limb function.
4. Therapeutic Ultrasound Machines
- Used to promote tissue healing and reduce pain through sound wave therapy.
5. Electrical Stimulation Units
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): Helps in pain management.
- NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation): Supports muscle strengthening.
6. Balance and Coordination Trainers
- Balance Boards and Stability Balls: Help improve core strength and balance.
7. Resistance Training Equipment
- Resistance Bands and Weights: Assist in strength training during rehabilitation.
8. Assistive Devices for Daily Living
- Grab Bars and Shower Chairs: Enhance safety and independence in daily activities.
9. Virtual Reality Therapy Systems
- Provide engaging rehabilitation exercises in a virtual environment, promoting motivation and engagement.
10. Cooling and Compression Devices
- Cryotherapy Devices: Reduce swelling and pain.
- Compression Garments: Improve circulation and reduce swelling.
Additional Considerations
Devices should be tailored to individual needs and conditions. It’s essential to work with healthcare professionals to determine the best devices and strategies for rehabilitation.