Surgical robotics (Robotic Exoskeleton) may be the first thing to come to mind when thinking about high-impact healthcare technology investments. Major factors driving the global Neurorehabilitation growth include the increasing prevalence of neurological diseases such as brain stroke, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, and our ageing population.
Here are the technical tools for Neurorehabilitation:
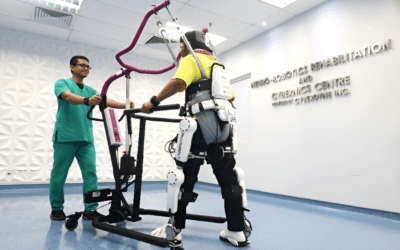
Robotic exoskeletons:

These wearable devices assist patients in moving their limbs and can be programmed to provide targeted therapy to specific muscle groups. Example: Cyberdyne, ReWalk Robotics produces the ReWalk Personal Exoskeleton, which provides powered hip and knee motion to help individuals with spinal cord hip injuries stand and walk.
Brain-computer interfaces:
These systems use electrodes implanted in the brain to allow individuals to control devices, such as a computer cursor, using their thoughts. Brain Gate, for example, produces implantable devices that allow individuals with spinal cord injuries and other neurological conditions to control assistive technology using their thoughts.
Electrical stimulation:
This technique involves applying low-level electrical currents to the brain or muscles to improve motor function or reduce muscle spasticity. Bioness, for example, produces the L300 Go, a functional electrical stimulation device that is designed to help individuals with foot drop caused by multiple sclerosis, or other neurological conditions.
Virtual reality (VR):
VR systems can be used to simulate real-world environments and provide interactive therapy for neurological conditions such as stroke and traumatic brain injury. Many virtual reality platforms, provide interactive therapy for stroke and traumatic brain injury patients.
Virtualists also create VR systems to provide interactive therapy for patients with stroke, traumatic brain injury, and MS. Their systems include the re-virtual system for upper extremity rehab, the Re Sight system for visual rehab, and the retrain system for cognitive rehab.
Virtual Reality Category
Of all of these technologies, Virtual Reality holds the most promise due to its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and proven outcomes.
Without visual attention, one cannot read, process information, or even feed one’s self. The patient is set up with a virtual reality game, where he/she can follow directions and sustain their attention for three minutes straight. So while the ultimate goal was to build grip, strength, and motor skills, sustained attention was an essential prerequisite for immediate progress. Without that foundation, a person can’t recover their other abilities.
Virtual Reality used In-Home can show the Greatest Patient Rehabilitative Effect

These are essential to build confidence and motivation in patients with significant neurological damage and pave the way for rebuilding additional skills.
When patients are trained on these technologies in a hospital or outpatient setting, and then taken home for continued therapy, therapists work with patients and meet them where they are (both skill-wise and geographically)
Home-based Virtual Reality therapy can offer an improved sense of control and engagement.
For healthcare provider organisations, the benefits of in-home Virtual Reality include providing high-dose, high-intensity, evidenced-based rehab five days a week, reduced length of stay, improved case mix to reduced no-shows at physical therapy appointments, and improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
It is rewarding to see patients with conditions that can often be demoralising having fun and making gains towards their recovery and gaining confidence.
Virtual Reality represents a paradigm shift in Neurorehabilitation due to its capacity to provide meaningful and realistic experiences that adapt learning principles to the intervention. Learning is improved when tasks are relevant and repetitive, and when task difficulty is gradually increased.
Conclusion:
In a jist, VR technology is a system that allows users to interact with images and sounds in the virtual environment, which can stimulate response and provide real-time feedback concerning their performance.