Neurological impairments that result in motor or cognitive disabilities are a common cause of adult-onset disability, affecting more than one billion people worldwide. This number is expected to increase in the coming years due to an ageing population.
In order to address the frequent lack of complete recovery, it is desirable to develop advanced neuro-rehabilitative treatments that are tailored to patients and more effectively target specific disabilities.
Neurological rehabilitation is a programme supervised by a doctor and designed for people with nervous system diseases, injuries, or disorders. This type of rehabilitation can often improve functionality, alleviate symptoms, and enhance the patient’s overall well-being.

The goal of a neurological rehabilitation programme is to improve physical, emotional, and social well-being and ultimately return the patient to the highest level of function and independence. Most patients can resume living independently, thus increasing their happiness and satisfaction with their lives.
Advanced technology, such as robot-assisted training, virtual reality, functional electrostimulation, and non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS), can enhance the intensity and quality of neurorehabilitation and manipulate brain excitability and plasticity. Innovative approaches, such as advanced technology, can also be used.
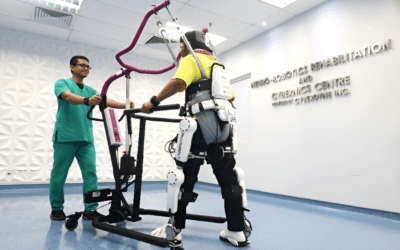
Robotic training can be controlled by the wearer’s intent to move. The product’s non-invasive sensors can detect faint “bio-electrical signals” that reflect the wearer’s intention on the surface of their skin. This unique system allows patients who have difficulty moving to perform their desired movements with their voluntary commands. The product’s elements can be precisely adjusted to fit all individuals, enabling comfortable and effective treatment. Both the wearer and their healthcare provider can gain unique insights into the signal patterns generated by the wearer and receive essential information such as the centre of balance and phases of the gait cycle, which helps shape the treatment course that aims to maximise neuroplasticity and ultimately gain more independence.
Virtual reality (VR) is the use of technology, such as a head-mounted display (HMD), tracking system, and sound device, to create an interactive three-dimensional (3D) experience. The ever-increasing capabilities of VR technology offer innovative treatment possibilities within the medical field, including the management of central nervous system disorders.

Functional electrostimulation (ES) of the central and peripheral nervous system can take advantage of intact neuromuscular systems to provide therapeutic exercise options, allow functional restoration, and manage or prevent medical complications following injuries. ES can restore upper extremity, lower extremity, and truncal functions, making many activities of daily living a potential reality for individuals with spine injuries. It can also help restore bladder and respiratory functions and prevent pressure ulcers, significantly decreasing morbidity and mortality following injury.
Non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS) can increase the excitability of targeted parts of the brain. When paired with individualised, task-specific, intense rehabilitation, it can lead to faster improvement in function than rehabilitation alone.
Products such as Cyberdyne HAL, Lightforce Lasers, and Vibramoov offer a complete solution for rehabilitation with leading technology! The Hybrid Assistive Limb [HAL], a powered exoskeleton suit developed by robotics company Cyberdyne, is designed to support and expand the physical capabilities of its users, particularly people with physical disabilities. Lightforce Lasers are smarter than the average lasers and designed to treat chronic conditions. Vibramoov stimulates neuroplasticity and regulates muscular activity, offering healthcare professionals a unique opportunity to preserve and enhance the sensory-motor functions of patients suffering from motor impairments.