In the realm of technological innovation, the integration of artificial intelligence into robotics marks a pivotal advancement with profound implications.
Robot ethics, sometimes known as “roboethics”, concerns ethical problems that occur with robots, such as whether robots pose a threat to humans in the long or short run, whether some uses of robots are problematic (such as in healthcare or as ‘killer robots’ in war), and how robots should be designed such that they act ethically.
Technological developments involving robotics and artificial intelligence devices are being employed evermore in elderly care and the healthcare sector more generally, raising ethical issues and practical questions warranting closer consideration of what we mean by “care” and, subsequently, how to design such software coherently with the chosen definition.
Robot ethics is a relatively new subdomain of robotics focused on ethical aspects of automation design and deployment.
Ethical Principles of Robot-Rehab Practise:

Developments in robotics and automation technologies are rapidly changing many aspects of our lives. The field of health care has been no exception, promising many boons while also bringing about controversial ethical questions.
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics in healthcare is a transformative development with immense promise for revolutionising patient care, diagnostics, and treatment modalities. These technologies can enhance the precision and efficiency of medical practises, improve patient outcomes, and increase the burden on healthcare professionals.
However, as AI and robotics become increasingly integrated into healthcare systems, a critical set of ethical implications emerges. These implications touch upon privacy, data security, accountability, transparency, fairness, and the preservation of human autonomy.
Understanding and addressing these ethical considerations are imperative to harness the full potential of AI and robotics in healthcare while ensuring the well-being and trust of patients, healthcare professionals, and society at large.
As AI and robotics continue to advance, several ethical considerations must be taken into account, including Bias and fairness.
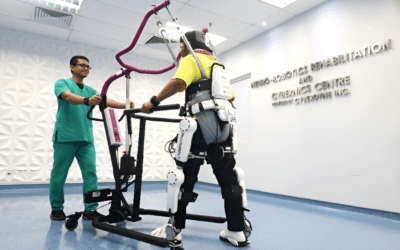
Robotic Rehabilitation

Beneficence: To do good to others; to promote the well-being of clients.
Fidelity: To be faithful; to keep promises and to honour the trust placed in rehabilitation counsellors.
Justice: To be fair in the treatment of all clients; to provide appropriate services to all. Nonmaleficence: Not to harm others.
As robots and AI systems become more autonomous, it can be difficult to determine who is responsible when things go wrong. Ethical considerations should be carefully understood and addressed as the field of advanced robotics and automation continues to advance.
At the individual-relational level, ethical intuitions involved supporting the autonomy of residents and care providers, using the robots to alleviate residents’ social isolation and the physical and psychosocial impacts associated with their use.
In both rehabilitation and assistance robotics, ethical considerations are paramount. Striking the right balance between assistance and robotic autonomy necessitates meticulous deliberation.
A well-developed care system that includes “bots” of all kinds should predict and balance the ethical impact equally not only between caregivers and receivers but for the system within which these actors function.