Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) usually results from a violent blow or jolt to the head or body. The degree of damage can depend on several factors, including the nature of the injury and the force of impact.
TBI also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. It can be classified based on the severity.
Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injury:
Traumatic brain injury can have wide-ranging physical and psychological effects. Some signs or symptoms may appear immediately after the traumatic event, while others may appear days or weeks later.
Mild injury
Physical symptoms:
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue or drowsiness
- Problems with speech
- Dizziness or loss of balance
Sensory symptoms:

- Sensitivity to light or sound
- Blurred vision, ringing in the ears, a bad taste in the mouth, or changes in the ability to smell
Cognitive symptoms:
- Loss of consciousness for a few seconds to a few minutes
- No loss of consciousness, but a state of being dazed, confused, or disoriented
- Memory or concentration problems
- Mood changes or mood swings
- Feeling depressed or anxious
- Difficulty sleeping
- Sleeping more than usual
Moderate to severe injuries
Moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries can include any of the signs and symptoms of mild injury, as well as these symptoms that may appear within the first hours to days after a head injury:
Physical symptoms
- Persistent headache or headache that worsens
- Repeated vomiting or nausea
- Convulsions or seizures
- Dilation of one or both pupils of the eyes
- Clear fluids draining from the nose or ears
- Inability to awaken from sleep
- Numbness in fingers and toes
- Loss of coordination
- Loss of consciousness from several minutes to hours
Cognitive symptoms

- Profound confusion
- Agitation
- Slurred speech
- Coma and other disorders of consciousness
In a child with traumatic brain injury, there may be
- Changes in eating or nursing habits
- Persistent crying and inability to be consoled
- Changes in ability to pay attention
- Changes in sleep habits
- Seizures
- Depression
- Drowsiness
- Loss of interest in their favourite toys or activities
Types of Traumatic Brain Injuries:
- Concussions
- Contusions
- Brain hemorrhages
- Intracranial haematomas
- Coup-contrecoup brain injury
- Diffuse axonal injury
- Penetrating brain injury
- Second impact syndrome
Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI):

Mild injury
Treatment may be needed on a short-term basis or throughout a person’s life. A variety of treatments can help a person recover from TBI and can sometimes eliminate certain physical, emotional, and cognitive problems associated with TBI. The specifics of treatment, including the type, setting, and length, depend on how severe the injury is and the area of the brain that was injured.
Mild traumatic brain injuries usually require no treatment other than rest and over-the-counter pain relievers to treat a headache.
Emergency
Emergency care for moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries focuses on making sure the person has enough oxygen and an adequate blood supply, maintaining blood pressure, and preventing any further injury to the head or neck.
People with severe injuries may also have other injuries that need to be addressed.
Medications
Medications to limit secondary damage to the brain immediately after an injury may include:
- Anti-seizure drugs
- Coma-inducing drugs
- Diuretics and
- Surgery
The impact on lives of patients with Brain Damage:

While recovery and rehabilitation are possible, most people with moderate to severe TBI face life challenges that will require them to adapt and adjust to a new reality.
After a brain injury, movement may be slow and can be worsened by other issues such as reduced balance, pain, and fatigue. A brain injury survivor with mobility problems may be unable to walk or partially walk with walking aids.
The cognitive effects of brain injury include attention and concentration problems, memory problems, and difficulty with motivation and making decisions. This may mean that people with a brain injury experience information overload and are slower at taking in and making sense of information.
They may have trouble with tasks that require multiple steps done in a particular order, such as laundry, driving, or cooking. Individuals with Traumatic Brain Injury may have difficulty recognising when there is a problem, which is the first step in problem-solving.
Challenges with work and completing once routine tasks can be much more difficult than before the injury. Some patients find that the skills and abilities that they used before the injury to meet these challenges are not as sharp as they once were.
Application of Rehabilitation Devices:

The effects of moderate to severe Traumatic Brain Injury can be long-lasting or even permanent. Rehabilitation therapies like physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech-language therapy, and assistive devices and technologies may help to strengthen patients to perform their activities of daily living.
After the acute care period of in-hospital treatment, people with severe TBI are often transferred to a rehabilitation centre where a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers helps with recovery.
The rehabilitation team includes neurologists, nurses, psychologists, and nutritionists, as well as physical, occupational, vocational, speech, and respiratory therapists.
Rehabilitation therapy may include:
- Physical therapy to build physical strength, balance, and flexibility and to help restore energy levels
- Occupational therapy to learn or relearn how to perform daily tasks, such as getting dressed, cooking, and bathing
- Speech therapy to improve the ability to form words, speak aloud, and use other communication skills; can include instruction on how to use special communication devices and treatment of trouble swallowing, called dysphagia
- Psychological counselling to learn coping skills, work on interpersonal relationships, and improve general emotional well-being; can include medication and other ways to address chemical imbalances that may result from TBI
- Vocational counselling to help a patient return to work and community living by finding appropriate work opportunities and ways to deal with workplace challenges
- Cognitive therapy to improve memory, attention, perception, learning, planning, and judgement. Cognitive Rehabilitation Therapy (CRT) is a strategy aimed at helping individuals regain their normal brain function through an individualised training programme. Using this strategy, people may also learn compensatory strategies for coping with persistent deficiencies involving memory, problem-solving, and the thinking skills to get things done. CRT programmes tend to be highly individualised and their success varies.
The Vital role of Rehabilitation Devices in recovery

Traumatic brain injury is gaining more attention because of its higher rates of morbidity and mortality.
Let’s learn about the different Rehabilitation Devices…
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):
The application of AI in the Rehabilitation of Traumatic Brain Injury mainly includes computer-assisted rehabilitation training, robotic-assisted rehabilitation training, virtual reality, brain-computer interfaces, transcranial magnetic stimulation, smart mobile technology and wearable assisted devices…
- Computer-Assisted Rehabilitation Training
Cognitive dysfunction is one of the main consequences of Traumatic Brain Injury. Cognitive impairment leads to a serious decline in the quality of life after TBI and is involved in the impact of depressive symptoms on emotional role functioning.
By far, computer-assisted rehabilitation training has been widely applied in the cognitive rehabilitation of people with Traumatic Brain Injury.
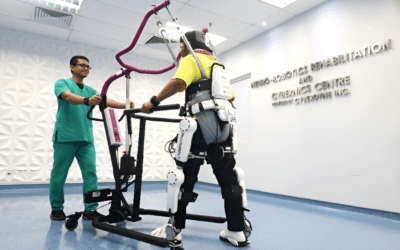
- Robotic-Assisted Rehabilitation Training
Rehabilitation robots have been rapid and vast developments. As a relatively young and rapidly developing field, rehabilitation robots are increasingly infiltrating the clinical environment. An increasing number of patients are suffering from limb motor dysfunction, which may be caused by stroke-related nerve damage, traumatic brain injury, or multiple sclerosis. The robotic-assisted rehabilitation therapy can deliver high-quality training to enhance the recovery process and promote the recovery of limb function
- Virtual Reality- (VR) Based Training
Virtual reality is a new and developing technology, that combines the characteristics of VR technology such as autonomy, interactivity, and existence with rehabilitation training.
VR is described as “an advanced human-computer interaction mode that allows users to interact naturally with a computer-based environment for training and full immersion. VR is now offering more new treatment measures for patients with Traumatic Brain Injury.
- Mobile Health Technology
Traumatic Brain Injury can lead to severe motor, cognitive, and emotional disturbance, and the rehabilitation of TBI is a long process. Fortunately, Mobile Health is an emerging technology, that can help manage patients with TBI better.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI)
Brain-computer interfaces (BCI) are developing into a possible method to replace the brain’s normal output pathways of peripheral nerves and muscles, and allowing paralytic patients to use a new method of communication and computer control, which has developed significantly over the past several decades.
Brain-computer interface (BCI) can convert brain signals obtained by non-invasive and invasive methods into control signals of some external devices, such as computer cursor or robot limb.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Disorders in memory and neural behaviour are a common sequence of Traumatic Brain Injury. studies show that low-field magnetic stimulation improved the cognitive and motor function of TBI more significantly.
- Wearable Assisted Devices
Wearable-assistive devices have been widely used in the rehabilitation of neurologicaldisorders such as traumatic brain injury.
Conclusion:
Traumatic brain injury and its related symptoms have become a major global health problem. Therefore, Rehabilitation of these Neurological disorders is aimed at improving the person’s ability to handle activities of daily living and to address cognitive, physical, occupational, and emotional difficulties.