Global Statistics
- Headaches: Over 10% of the global population experiences migraines.
- Epilepsy: More than 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy.
- Dementia: An estimated 47.5 million people are living with dementia, with 7.7 million new cases every year.
- Stroke: Over 6 million individuals die from stroke each year, with 80% of these deaths occurring in low- and middle-income countries.

Neuro rehabilitation and recovery for people with neurological disorders, such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative diseases, depend mainly on neuroplasticity, the brain’s capacity to restructure and adapt.
Neuroplasticity based treatments are also advantageous for neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. These conditions cause the progressive degradation of brain tissues, which worsens cognitive function, impairs movement and causes other distressing symptoms.
Understanding the mechanisms and principles of neuroplasticity lays the groundwork for creating novel strategies and treatments to speed healing and encourage functional recovery. Neuroplasticity-based therapies give people with neurological illnesses hope and promise by taking advantage of the brain’s extraordinary capacity to rearrange itself.
Innovative Strategies in Neuro Rehabilitation
Innovative Approaches promise to increase neuroplasticity and foster rehabilitation. These therapies can control neuroplasticity and improve motor, mental, and sensory functions…
Robotics
Robotic rehabilitation therapy offers highly controlled, repetitive, and intensive training. It reduces the physical burden for the physiotherapist and provides objective and quantitative assessments of patients’ progress throughout the rehabilitation process.

Robots for Neurorehabilitation are designed to support the administration of physical exercises to the upper or lower extremities, to promote neuro-motor recovery.
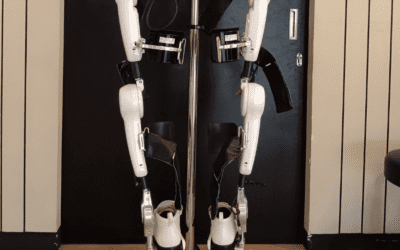
Portable exoskeletons
These are becoming revolutionary devices for gait rehabilitation, due both to the active participation required by the user which promotes their physical activity, and to the possibility of being used as an assistive device at home.
Exoskeletons are “wearable” systems that consist of a mechanical structure, electric motors, sensors, a computer, and batteries. In general, the operating principle of an exoskeleton for gait rehabilitation is based on the information captured by sensors and advanced algorithms; the computer detects the user’s intention to take a step. Once detected, the computer plans the type of movement that the exoskeleton must carry out to take the step and sends this information to the motors, which are responsible for executing this movement in synergy with the user.

Non-invasive brain stimulation
The brain is a dynamic organ that is sensitive to internal and external environmental changes. In recent years, neuroscience has gained a better understanding of these mechanisms of neural plasticity.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and electrical brain stimulation are non-invasive techniques that allow us to modulate some of these neural changes safely and painlessly. They can be combined with other techniques, to improve their effectiveness.
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality is a useful cutting-edge tool that can assess virtual scenarios used for motor rehabilitation and intervene in them. Virtual reality devices can detect the user’s orientation with a high level of precision.
Virtual reality is, therefore, a field of innovation and translational research applied to clinical practise, which, when correctly used, configured, and supervised by professionals, contributes to the patient’s recovery.
Neural Interfaces
Neural interfaces are engineering solutions aimed at restoring brain connections that allow the body to re-coordinate and promote people’s recovery. They are based on the fact that human neuronal systems generate, transmit, and process electrochemical signals, part of which can be interpreted and stimulated.
Monitoring
This is a promising technology based on portable or wearable sensors, such as accelerometers and inertial measurement units that can be connected in different anatomical places, allowing the type, quantity, and quality of daily activities and therapy to be monitored. Objective, continuous, and sensitive data related to the rehabilitation process are obtained through this assessment tool.

Rehab therapies such as Cyberdyne Technology, Lightforce Lasers, and Vibramoov are dedicated to achieving the best possible outcomes for patients. That means providing access to the most qualified, experienced, and caring clinicians. It also means maintaining a focus on advancements in technology that can benefit patients.
The Wearable Cyborg HAL by Cyberdyne is designed to improve physical functions in patients with disorders of the limbs. The Hybrid Assistive Limb improves locomotor activity in patients with disabilities.
Lightforce Therapy Lasers are unique among laser devices with a singular focus on rehabilitation and pain management.
Vibramoov Technology preserves sensory-motor interaction, enhances coordination, and promotes motor recovery. Vibramoov is an effective and innovative therapeutic solution used in functional rehabilitation.
Source: This information is based on the WHO’s 2023 action plan
Free Summary Download (PDF)