Injuries to the spinal cord result in partial or complete loss of sensory, motor, or autonomic function. They can be caused by trauma (such as accidents, falls, or sports injuries) or non-traumatic factors (such as diseases or infections).
Symptoms
- Loss of movement or sensation in the limbs
- Changes in reflexes
- Numbness or tingling
- Breathing difficulties (especially with high cervical injuries)
- Loss of bowel or bladder control
- Chronic pain or spasticity
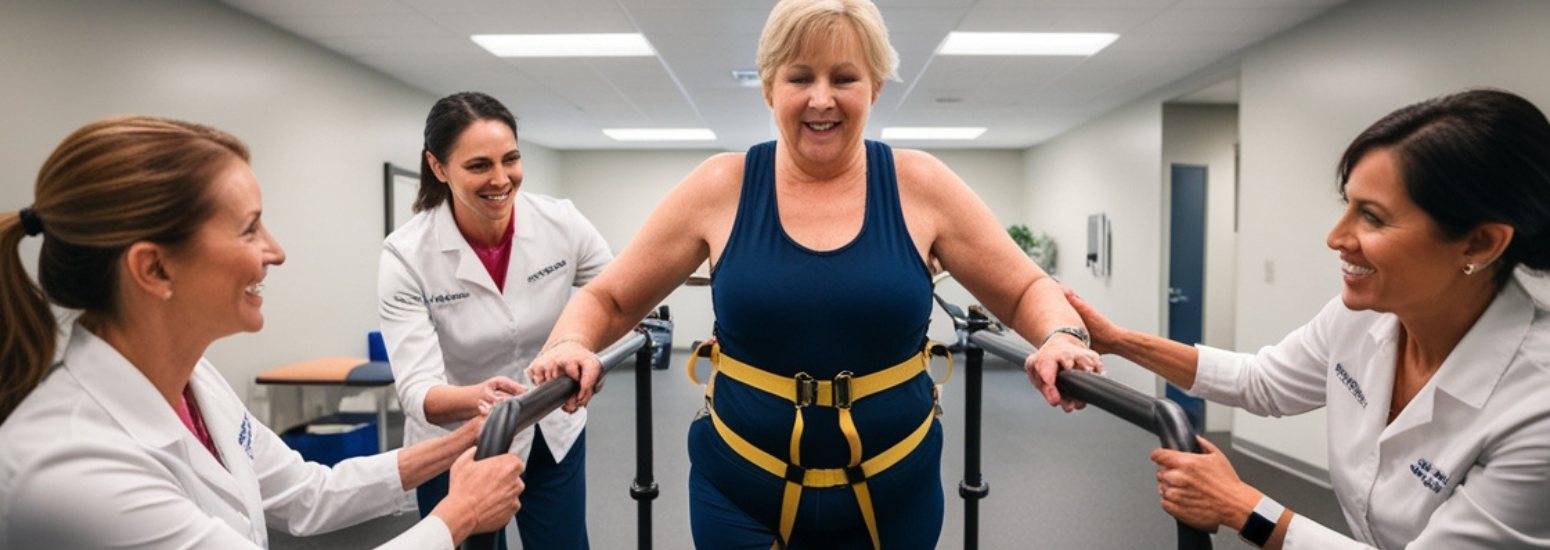

Neurorehabilitation for Spinal Cord Injuries and Pain Relief: Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis: SCIs are diagnosed through clinical evaluations, MRI, CT scans, and X-rays to assess the extent of injury and locate damage.
Treatment:
- Emergency Care: Immediate stabilization and transport to a medical facility.
- Surgery: May be required to remove bone fragments, and hematomas, or to stabilize the spine.
- Rehabilitation: Focuses on regaining function and independence, using physical, occupational, and Neurorehabilitative therapies.
Long-term Effects
The long-term consequences of SCIs can vary widely and may include:
- Ongoing mobility challenges
- Complications such as pressure sores, respiratory infections, and urinary tract infections
- Psychological impacts, including depression and anxiety
- Need for assistive devices and modifications in living environments
So, how Does Neurorehabilitation aid in recovery after a spinal cord injury?
Neurorehabilitation plays a crucial role in recovery after a spinal cord injury (SCI) by facilitating physical, emotional, and functional recovery.

Here are several ways in which Neurorehabilitation aids this process…
1.Physical Therapy for Motor Recovery and Pain Reduction in Neurorehabilitation for Spinal Cord Injuries and Pain Relief
Neurorehabilitation focuses on regaining motor skills through targeted exercises. Physical therapy may involve:
- Strengthening Exercises: Building muscle strength in affected areas to improve mobility.
- Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): Applying electrical currents to stimulate paralyzed muscles, enhancing movement and preventing muscle atrophy.
2. Improving Mobility and Gait
Gait training is an essential aspect of Neurorehabilitation. Techniques include:
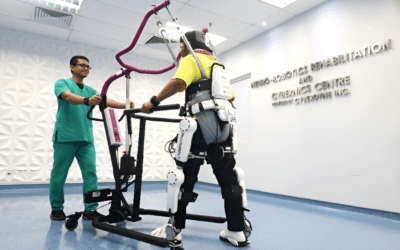
- Robotic-Assisted Therapy: Using robotic devices or body-weight-supported treadmills to help patients relearn walking patterns.
- Task-Specific Training: Practicing walking and other functional movements to promote neural pathways and muscle memory.
3. Enhancing Balance and Coordination
Balance training is vital for preventing falls and promoting independence. Neurorehabilitation may include:
- Balance Exercises: Activities on unstable surfaces or with balance equipment to improve stability.
- Proprioceptive Training: Activities that enhance body awareness and control, essential for coordinated movement.
4. Occupational Therapy
Neurorehabilitation incorporates occupational therapy to help individuals regain the ability to perform daily activities. This may involve:
- Adaptive Strategies: Teaching techniques to accomplish tasks with limited mobility.
- Assistive Devices: Using tools and equipment to facilitate independence in activities of daily living (ADLs), such as dressing and cooking.
5. Pain Management and Spasticity Reduction
Neurorehabilitation addresses pain and muscle spasticity through:
- Therapeutic Modalities: Techniques like heat, cold, and electrical stimulation to relieve pain.
- Stretching and Range of Motion Exercises: Reducing spasticity and improving flexibility in affected muscles.
6. Psychological Support
Recovering from an SCI can be emotionally challenging. Neurorehabilitation provides:
- Counseling and Support Groups: Helping individuals cope with changes in their physical abilities and emotional well-being.
- Motivational Strategies: Encouraging a positive mindset and setting achievable goals throughout the rehabilitation process.
7. Education and Self-Management
Neurorehabilitation equips patients with knowledge about their condition, self-care techniques, and strategies for managing secondary complications, such as pressure sores and urinary tract infections.
Conclusion
Neurorehabilitation is a comprehensive approach to recovery after a spinal cord injury, focusing on physical rehabilitation, functional independence, and emotional support. Through personalized therapy programs, individuals can regain mobility, enhance their quality of life, and adapt to the challenges presented by their injuries. With advances in rehabilitation techniques and technologies, patients can achieve significant improvements in their daily functioning and overall well-being.
Spinal cord injuries are complex conditions that require a multidisciplinary approach to management and rehabilitation. Early intervention and comprehensive care can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by SCIs. Advances in medical science and technology continue to enhance recovery options and support for those living with these injuries.