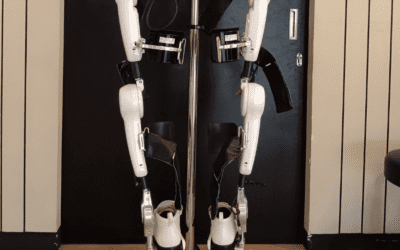
Cyberdyne HAL® helps people who have lost the use of their lower limbs, rediscover the joy of walking. The robotic suit uses the patient’s intention to move the legs. In patients with orthopaedic injuries, Cyberdyne’s – Hybrid Assistive Limb, HAL® improves their locomotor activities.
How Does HAL Work?

When a Orthopaedic Injury person tries to move, the brain sends a signal to the muscle to command the movement. At that time, a very faint signal that reflects the wearer’s intention to move appears on the skin’s surface. Using its sensors attached to the skin’s surface, the Wearable Cyborg™ HAL® detects these so-called “bio-electrical signals” to perform the desired movements with the wearer’s voluntary commands.
- When we move our bodies, we begin by thinking about the movement.
By thinking, “I want to walk,” the brain sends the necessary signals through the nerves to the muscles needed for that movement. - In the body of a healthy person, each muscle receives signals sent from the brain, allowing the muscles to move only the amount of force necessary to match the intention.
- As the signals travel towards the muscles, they leak on the skin surface as very faint signals, so-called “bio-electric signals [BES]”. HAL can read the BES with its originally developed electrodes attached to the wearer‘s skin surface. Based on various other information obtained as well, HAL determines the wearer’s desired movements.
- The Wearable Cyborg™ HAL® controls the power unit according to the movements it recognises to assist the wearer in moving according to his or her intentions or even exerting more force than usual.
- Once the movement is complete, the brain cheques how the body moved according to the signals sent. When HAL realises the wearer‘s intended motion, the body feeds back information of the successful movement. This allows the brain to gradually learn how to send out the signals necessary for good movements. Repeating this process could help a person with a disability improve their physical function after taking off HAL®
Locomotion with Orthopaedic Injury patients

Exoskeletons/Rehabilitation robots in physical therapy are used for treating disabilities such as neurological disorders, spinal cord injuries, cerebral palsy, and gait disorders in orthopaedic injury in general. Exoskeletons increase capabilities; assist locomotion and rehabilitation of patients with orthopaedic injury.
At Cyberdyne, we provide advanced neuro-robotic rehabilitation technologies for the well-being of patients around the world. Our mission is simple – we empower individuals to walk on their own using HAL®, our non-invasive technology solution.
HAL® has a wide range of applications, such as improving physical function in welfare and medical fields, heavy work support in other workplaces, and supporting recovery activities at disaster sites.
In the process of Orthopaedic Injury patient rehabilitation, Robots are used in-
- Lower and upper limb exercise
- As assistive devices
- Lower and upper limb wearable devices
Learn how individuals around the world use Cyberdyne technology to regain their mobility and restore their independence.
Connect with us at https://rehabmodalities.com/ to learn more about our healthcare platform that connects the ‘Human and the Robot’